Impact of Processing on Nutritional Value

Shredded mexican cheese nutrition – Processing significantly impacts the nutritional profile of Mexican cheese. Methods like shredding and pasteurization, while enhancing convenience and shelf life, can affect the cheese’s nutrient content, sometimes leading to losses or alterations in bioavailability. Understanding these changes is crucial for consumers making informed choices about their diet.The transformation of a solid block of Mexican cheese into shredded form involves mechanical processes that can affect its nutritional composition.
Similarly, pasteurization, a heat treatment used to eliminate harmful bacteria, can also impact the delicate balance of nutrients within the cheese.
Nutritional Differences Between Shredded and Block Cheese
Shredded Mexican cheese generally possesses a similar overall nutritional profile to its block counterpart, but subtle differences exist. While the total fat, protein, and calorie content remain relatively consistent, some minor nutrient losses can occur during the shredding process. Exposure to air and light during shredding can lead to oxidation of certain vitamins, such as vitamin A and vitamin E, potentially reducing their levels compared to the protected environment within a sealed block of cheese.
Shredded Mexican cheese, a staple in countless dishes, offers a sharp, salty tang but its nutritional profile can vary widely. Understanding the fat and sodium content is crucial, especially when comparing it to other cheese options like the processed varieties. For instance, a quick look at the nutritional breakdown of sargento string cheese nutrition reveals a different composition, often lower in fat but potentially higher in sodium.
Ultimately, both shredded Mexican and string cheese choices demand mindful consideration within a balanced diet.
Furthermore, the increased surface area of shredded cheese might contribute to a slightly faster rate of nutrient degradation over time.
Effects of Pasteurization on Mexican Cheese Nutrients, Shredded mexican cheese nutrition
Pasteurization, while essential for food safety, can lead to some nutrient loss in Mexican cheese. Heat treatment can denature certain heat-sensitive proteins, reducing their bioavailability. While the impact on the overall protein content might be minimal, the body’s ability to effectively utilize these proteins might be slightly diminished. Similarly, some vitamins, particularly water-soluble ones, may be degraded by heat, although the extent of this loss is often dependent on the specific pasteurization parameters employed.
Different pasteurization methods (e.g., high-temperature short-time vs. ultra-high temperature) can also result in varying degrees of nutrient retention.
Potential Nutrient Losses During Shredding and Pasteurization
The following bullet points summarize the potential nutritional differences between differently processed Mexican cheeses:
- Vitamin Loss: Shredding and pasteurization can lead to some loss of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) and water-soluble vitamins (B vitamins, C) due to oxidation and heat degradation. The extent of loss varies depending on processing conditions and storage.
- Protein Denaturation: Heat treatment during pasteurization can denature some proteins, reducing their digestibility and bioavailability, although the overall protein content remains largely unchanged.
- Moisture Content: Shredding might lead to slightly increased moisture loss compared to block cheese due to increased surface area, potentially affecting the concentration of certain nutrients.
- Microbial Changes: Pasteurization eliminates harmful bacteria, but it also reduces beneficial bacteria, which might have minor impacts on the overall gut health benefits of cheese, although this is a complex area of research.
Health Implications and Considerations: Shredded Mexican Cheese Nutrition
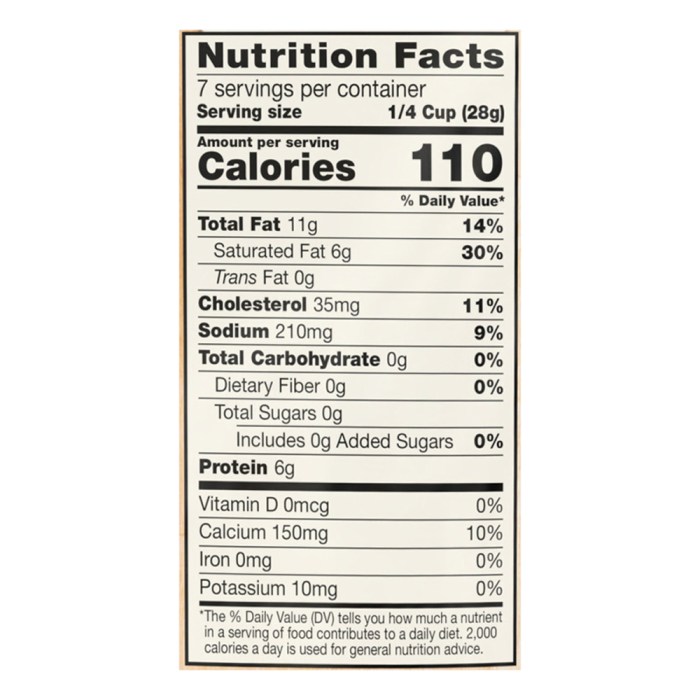
Shredded Mexican cheese, a popular addition to many dishes, presents a complex nutritional profile with both potential benefits and drawbacks. Understanding its impact on health requires a balanced perspective, considering both the positive contributions of essential nutrients and the potential negative effects of excessive consumption. Moderate inclusion within a balanced diet is key to maximizing benefits and minimizing risks.Shredded Mexican cheese offers a significant source of calcium, crucial for maintaining strong bones and preventing conditions like osteoporosis.
Calcium is essential for bone growth and density throughout life, particularly important during childhood and adolescence, and for maintaining bone health in adulthood and preventing age-related bone loss. Furthermore, Mexican cheese often contains other essential nutrients, although the exact amounts vary depending on the type of cheese and processing methods. However, these benefits must be weighed against potential negative impacts.
Saturated Fat and Cholesterol
Excessive consumption of shredded Mexican cheese poses risks due to its high saturated fat content. Saturated fats can elevate LDL cholesterol (“bad” cholesterol) levels in the blood, increasing the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular problems. The American Heart Association recommends limiting saturated fat intake to less than 10% of total daily calories. A typical serving of shredded Mexican cheese can contribute a significant portion of this daily limit, underscoring the importance of mindful consumption.
For example, one ounce of cheddar cheese, a common type used in Mexican cheese blends, contains approximately 7 grams of saturated fat. Consuming several ounces daily could quickly exceed recommended limits.
Shredded Mexican Cheese in a Balanced Diet
Incorporating shredded Mexican cheese into a balanced diet requires moderation and awareness. It can be a valuable source of calcium and flavor, but should not be the primary source of these nutrients. A balanced approach includes prioritizing lean protein sources, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, while limiting processed foods and saturated fats. Using shredded Mexican cheese as a flavorful garnish or in smaller portions rather than as a main ingredient can help control saturated fat intake.
For example, sprinkling a small amount over a salad or using it sparingly in tacos, instead of heavily layering it, is a healthier approach. Careful portion control and mindful consumption are key to enjoying the flavor and nutritional benefits of shredded Mexican cheese without compromising overall health.
Essential FAQs
Is all shredded Mexican cheese created equal?
Nope! Nutritional content varies depending on the type of cheese (cheddar, Monterey Jack, etc.) and the processing methods used.
Can I eat shredded Mexican cheese if I’m lactose intolerant?
It depends on your level of intolerance. Some individuals can tolerate small amounts, while others should avoid it altogether. Lactose-free options are available.
Does shredded Mexican cheese have a lot of sodium?
Yes, many varieties are relatively high in sodium. Check nutrition labels and consider choosing lower-sodium options.
Is shredded Mexican cheese a good source of protein?
Yes, it’s a decent source of protein, contributing to satiety and muscle building.



